Lua programming is a powerful and versatile tool for developers across industries, but understanding its Lua keywords is crucial for success. This guide dives deep into the practical applications, examples, and use cases of Lua keywords, helping you unlock their full potential for your projects.
1. The Role of Lua Keywords in Programming
Lua keywords are the reserved words in the Lua language that define the syntax and structure of scripts. These keywords are immutable and cannot be used as identifiers, ensuring clarity and consistency in programming.
Common Examples of Lua Keywords
Some essential Lua keywords include:
if,then,else: For conditional logic.for,while,repeat: For loops and iterations.function,return: For defining and managing reusable code.local,nil: For variable scope and absence of values.
Why Are Lua Keywords Essential?
- Syntax Integrity: They provide a structured way to write code, reducing ambiguity.
- Code Readability: Keywords ensure code is understandable by anyone familiar with Lua.
- Error Prevention: Improper use of Lua keywords immediately triggers syntax errors, guiding developers to fix issues quickly.
2. Categories of Lua Keywords
2.1 Control Flow Keywords
Control flow keywords dictate the logic and structure of your program. Examples include:
if,then,else: For conditional statements.for,while,repeat: For managing loops.
Example: Conditional Statements
Example: Loops
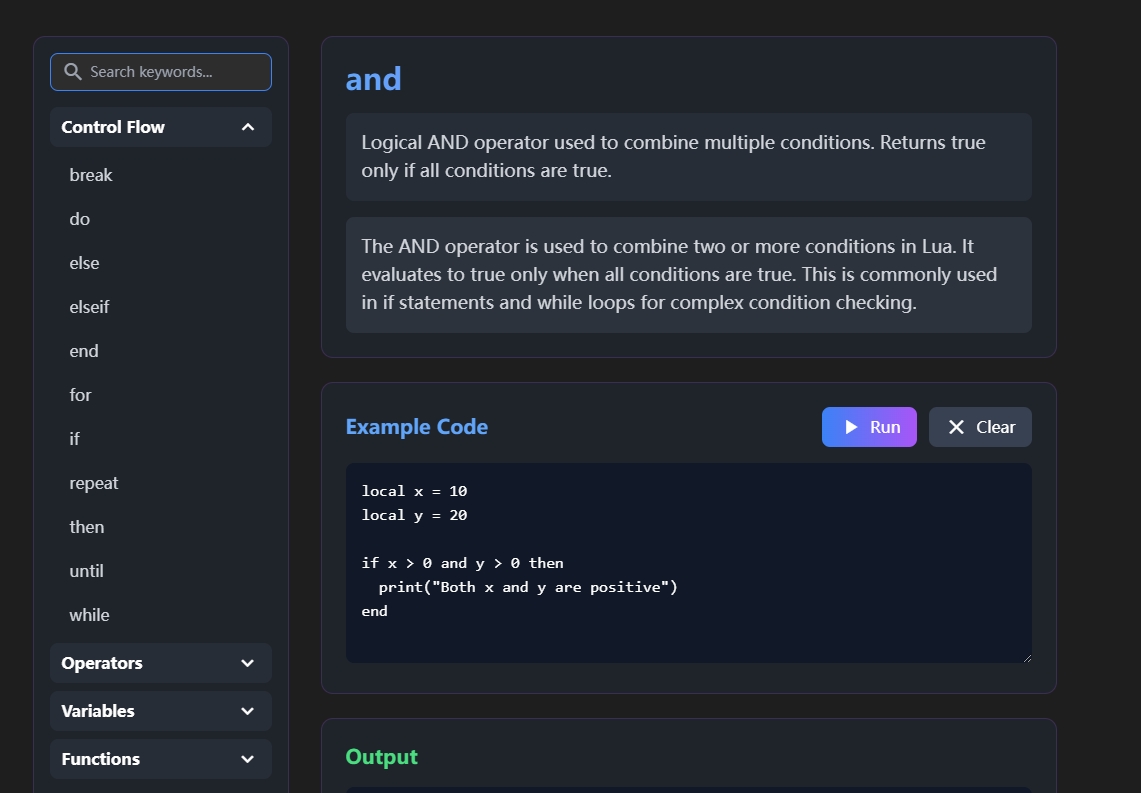
2.2 Logical Operators
Logical operators like and, or, and not are used to combine or negate conditions.
Example: Combining Conditions
2.3 Variable and Function Keywords
local: Limits variable scope to prevent interference with global variables.function: Declares reusable blocks of code.return: Returns values from functions.
Example: Function Declaration
2.4 Value Keywords
nil: Represents the absence of a value.true,false: Boolean values for logical expressions.
Example: Using nil
3. Practical Use Cases of Lua Keywords
3.1 Game Development
Game engines like Roblox and Corona heavily rely on Lua keywords to handle player actions, events, and animations. Keywords like if, for, and function are central to scripting these mechanics.
Example: Simple Game Script
3.2 Data Processing
Loops and conditionals in Lua are invaluable for data filtering and analysis. Lua keywords like while and repeat ensure efficient data handling.
Example: Data Iteration
3.3 Automation Scripts
Automating tasks becomes simpler with Lua keywords, particularly for repetitive or conditional operations.
Example: Automation Script
4. Best Practices for Using Lua Keywords
4.1 Limit Scope with local
Always use the local keyword for variables to avoid polluting the global scope.
4.2 Combine Keywords Efficiently
Combine control flow and logical keywords for streamlined logic.
Example: Combined Logic
4.3 Test and Debug
Use simple scripts to test complex Lua keywords logic and avoid runtime errors.
5. Avoiding Common Mistakes with Lua Keywords
5.1 Overwriting Reserved Words
Never attempt to use a Lua keyword as a variable name.
5.2 Infinite Loops
Ensure your while and repeat loops have valid exit conditions.
5.3 Misusing nil
Always check for nil before accessing variables to prevent unexpected errors.
6. Advanced Keyword Techniques
6.1 Nested Loops
Use nested loops for complex iterations, but keep readability in mind.
Example: Nested Loops
6.2 Chaining Conditions
Chain and and or for concise decision-making.
7. Staying Updated with Lua Keywords
Lua evolves with each version, and staying informed about changes to Lua keywords is essential for compatibility. Keep track of updates by visiting Lua’s official documentation and community forums.
Conclusion
Mastering Lua keywords unlocks the potential of Lua programming for projects ranging from game development to data processing. With their robust functionality and straightforward syntax, these building blocks are invaluable for creating efficient, maintainable code. By practicing their use, avoiding common mistakes, and exploring advanced techniques, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a Lua expert. Start exploring today and elevate your programming skills!