Understanding Lua all keywords is essential for anyone looking to master this lightweight yet powerful programming language. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, knowing these keywords inside out will help you write clean, efficient, and functional code. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about Lua all keywords, providing practical examples, insights, and tips.
🚀 What Are Keywords in Lua?
In Lua, keywords are reserved words that have predefined meanings. They form the core of the language and are essential for its syntax and structure. You cannot use these words as identifiers, such as variable names, function names, or table keys.
Why Learn Lua All Keywords?
-
Essential Syntax Understanding: Keywords define the grammar of Lua.
-
Avoid Errors: Using a keyword as a variable name will cause syntax errors.
-
Efficient Coding: Understanding these keywords enhances your ability to write concise and effective code.
For example:
local function = "test" -- Syntax error: 'function' is a keyword📝 Full List of Lua All Keywords
Lua has a relatively small set of keywords, making it beginner-friendly. Here is the list of Lua all keywords:
-
and -
break -
do -
else -
elseif -
end -
false -
for -
function -
goto -
if -
in -
local -
nil -
not -
or -
repeat -
return -
then -
true -
until -
while
These keywords are integral to Lua’s functionality, allowing you to control flow, declare variables, and execute logic effectively.
🔍 Deep Dive Into Lua All Keywords
📘 Control Flow Keywords
Control flow keywords determine the flow of execution in your Lua programs.
if, elseif, else
These keywords allow conditional branching.
Example:
if x > 0 then
print("Positive number")
elseif x == 0 then
print("Zero")
else
print("Negative number")
endfor, while, repeat, until
Use these keywords for loops.
Example:
for i = 1, 5 do
print(i)
end
local x = 0
while x < 5 do
x = x + 1
print(x)
end
repeat
x = x - 1
print(x)
until x == 0📗 Logical Keywords
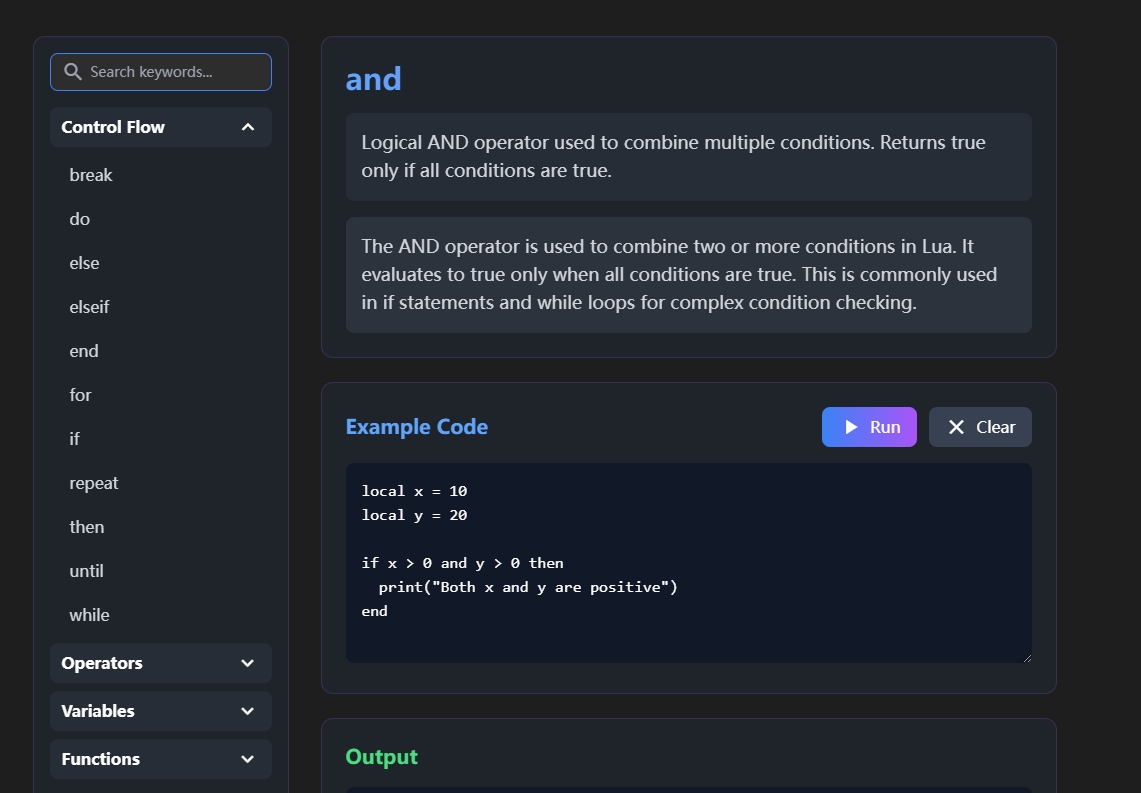
and, or, not
These logical operators are essential for constructing conditions.
Example:
if x > 0 and x < 10 then
print("Single digit positive number")
end
if not x then
print("x is nil or false")
end📙 Variable and Value Keywords
local
Defines a variable with local scope, crucial for maintaining clean and modular code.
Example:
local count = 0
for i = 1, 10 do
local temp = i * 2
count = count + temp
end
print(count)nil
Represents the absence of a value, useful for initializing or clearing variables.
Example:
local value = nil
if value == nil then
print("Value is undefined")
endtrue, false
These Boolean values are the foundation of logical operations.
Example:
local isActive = true
if isActive then
print("The system is active")
else
print("The system is inactive")
end🛠️ Practical Applications of Lua All Keywords
✅ Declaring Functions with function
The function keyword is used to define reusable blocks of code.
Example:
function greet(name)
print("Hello, " .. name)
end
greet("Lua Developer")Functions in Lua can also be anonymous, allowing more flexibility:
local greet = function(name)
print("Hi, " .. name)
end
greet("World")🔄 Looping with for and while
Iterate through tables or perform repetitive tasks.
Example:
table_data = {"Lua", "Python", "JavaScript"}
for i, v in ipairs(table_data) do
print(i, v)
end
local index = 1
while index <= #table_data do
print(table_data[index])
index = index + 1
end🌐 Leveraging local for Variable Scope
Use local to limit the scope of a variable to a specific block or function.
Example:
local x = 10
function calculate()
local y = 20
return x + y
end
print(calculate()) -- Output: 30🧩 Common Mistakes When Using Lua All Keywords
❌ Misusing Reserved Words
Attempting to use keywords as variable names leads to errors.
Example:
local return = 5 -- Syntax error🛑 Forgetting end
Each block that starts with a keyword like if, for, or function must end with end.
Example:
if x > 0 then
print("Positive")
-- Missing 'end' will throw an error🔍 Misunderstanding nil
The nil keyword represents the absence of a value. Be cautious when using it to avoid unintended behavior.
Example:
local value = nil
if value == nil then
print("Value is undefined")
end📊 Comparison: Lua Keywords vs Other Languages
| Language | Number of Keywords | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Lua | 21 | and, function, nil |
| Python | 35 | if, else, lambda |
| JavaScript | 64 | if, function, class |
Why Lua’s Simplicity Stands Out
Lua’s small number of keywords makes it easier to learn and reduces the cognitive load compared to other programming languages. This simplicity makes it a favorite for embedding in applications and creating efficient scripts.
💡 Tips for Mastering Lua All Keywords
-
Practice Regularly: Write small scripts to use different keywords.
-
Debug Actively: Pay attention to error messages related to keywords.
-
Use Documentation: Lua’s official manual is an excellent resource.
-
Experiment: Test the limits of each keyword to understand its scope and behavior.
-
Collaborate: Discuss coding challenges with peers to learn new insights.
-
Build Projects: Apply these keywords in real-world scenarios to strengthen your understanding.
-
Explore Libraries: Many Lua libraries utilize keywords effectively—studying their code can provide valuable insights.
-
Join Communities: Participate in Lua forums or GitHub projects to gain practical experience.
🌟 Final Thoughts on Lua All Keywords
Mastering Lua all keywords opens up endless possibilities in game development, scripting, and automation. By familiarizing yourself with these 21 keywords and practicing their use, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a proficient Lua programmer.
To elevate your expertise further, dive deeper into real-world projects where these keywords come into play. As you gain experience, you’ll appreciate the elegance and efficiency that Lua’s concise keyword set brings to programming. Whether you are building a game, creating scripts for automation, or embedding Lua into an application, a solid grasp of Lua all keywords is your foundation for success.
With consistent practice, collaboration, and exploration, the full potential of Lua can be unlocked. So, take the first step, and immerse yourself in the fascinating world of Lua programming today!